В настоящее время в лечебно-профилактических учреждениях активно внедряются медицинские информационные системы (МИС), и количество таких систем неуклонно растет [1, 2].
Информация, обрабатываемая в МИС, включает в себя персональные данные пациентов, представляющие собой медицинскую тайну. Следовательно, доступ к такой информации должен быть ограниченным и строго контролируемым [3].
Наиболее надежным с точки зрения безопасности является подход, подразумевающий проверку прав доступа пользователей на уровне БД. Во многих СУБД для этого применяются встроенные средства контроля доступа (СКД), в основе которых лежит комбинация дискреционной и ролевой моделей безопасности. В данном случае в качестве защищаемых объектов выступают объекты БД (таблицы, представления и пр.), в качестве субъектов безопасности – пользователи или группы пользователей МИС, а для каждой пары «субъект безопасности–защищаемый объект» явно задается список разрешенных операций (вставка, выборка, редактирование, удаление) [4, 5].
Однако применение такого подхода к защите данных в МИС в чистом виде является недостаточным и неудобным.
Прежде всего это связано со специфическими особенностями МИС, к которым можно отнести зависимость прав доступа и большое количество защищаемых объектов.
Права доступа зависят от следующих факторов:
- время доступа к данным; по прошествии определенного времени доступ на изменение ранее сделанной записи должен быть закрыт;
- текущие взаимоотношения врач–пациент–лечащий врач; на время лечения пациента врач должен получить доступ к его медицинским данным в полном или ограниченном объеме;
- статус пациента; доступ к информации ряда пациентов должен быть ограничен независимо от других факторов;
- место пребывания пациента; некоторые сотрудники подразделения, в которое переводится пациент, должны получать доступ к медицинским данным пациента в полном или ограниченном объеме;
- степень конфиденциальности информации; доступ к некоторым медицинским данным пациента должен быть открыт только узкому кругу лиц независимо от других условий.
Большое количество защищаемых объектов – доступ в МИС должен ограничиваться не только на уровне таблиц, но и на уровне записей [6–8].
Также примем во внимание требование предоставлять врачу доступ только к строго ограниченному объему информации о пациенте, которая ему нужна в данный момент времени для выполнения своих должностных обязанностей.
Таким образом, для обеспечения этого требования с учетом особенностей, указанных выше, необходимо практически постоянно переопределять права доступа пользователей МИС к данным пациента [9].
Учитывая огромное количество защищаемых объектов в МИС, можно сделать вывод, что обеспечить такой режим работы штатными средствами весьма затруднительно. В любом случае объем работы администратора безопасности существенно увеличится, что неизбежно приведет к ошибкам и несвоевременному переназначению прав доступа [10].
Таким образом, актуальной является задача модификации стандартного механизма СКД в МИС с целью избавления администратора безопасности от большого объема рутинной работы.
Для достижения поставленной цели прежде всего необходимо разработать модель системы безопасности обобщенной МИС.
Формальное описание новой модели
С учетом требований к модели разграничения доступа в МИС была разработана следующая модель.
Основные элементы: S – множество субъектов; G − множество групп субъектов; O – множество объектов (права доступа на некоторые объекты могут быть заданы явно, для остальных объектов права определяются динамически); ACL – множество списков контроля доступа (для явного задания прав); {g, o, {r}} – список контроля доступа; R − множество прав доступа; (L, £) – решетка уровней конфиденциальности; {O, tсозд, tпред} – метка времени, представляющая собой объект, время его создания, предельное время доступа к нему; N – множество меток времени (определяют предельное время изменения объекта); n:O®tпред – функция, возвращающая значение времени, по истечении которого доступ на изменение объекта o прекращается; c:S, O®R – функция, определяющая для каждого субъекта права доступа на определенный объект в зависимости от взаимоотношений между ними; PGÍG – множество привилегированных групп, члены которых имеют полный доступ ко всем объектам; PA:G, O®R – функция, определяющая множество прав r группы g на объект o; SAsÍG – множество групп, к которым принадлежит субъект; group:S®SAs – функция, определяющая множество групп, к которым принадлежит субъект s; Avail:S, O, R ® 1,0 – функция, определяющая доступность права r субъекта s на объект o; q(S, O, G, PG, L, N, ACL) – состояние системы; Q – множество состояний системы.
Операторами, используемыми в данной модели, являются следующие.
● Создать объект o¢ с уровнем конфиденциальности lo, меткой времени {O, tсозд, tпред}. Условие выполнения: o¢ÏO, loÎL. Новое состояние системы: S¢=S, O¢=OÈ{o¢}, G¢=G, PG¢=PG, L¢=L, N ¢=NÈ{noc}È{nol}, ACL¢=ACL.
● Создать группу g¢ с уровнем конфиденциальности lr, множеством прав доступа {r} на объекты {o¢}. Условие выполнения: gÏG, lrÎL. Новое состояние системы: S¢=S, O¢=O, G¢=GÈ{g¢}, PG¢=PG, L¢=L, N¢=N, ACL¢=ACLÈ{g¢, {o¢}, {r}}.
● Добавить право доступа r¢ группы g¢ на объект o¢ путем изменения/добавления списка контроля доступа acl¢. Условие выполнения: g¢ÎG, r¢ÎR. Новое состояние системы: S¢=S, O¢=O, G¢=G, PG¢=PG, L¢=L, N¢=N, ACL¢=ACLÈ{acl¢}.
● Удалить право доступа r¢ группы g¢ на объект o¢ путем изменения/удаления списка контроля доступа acl¢. Условие выполнения: {g¢, o¢, r¢}ÎACL. Новое состояние системы: S¢=S, O¢=O, G¢=G, PG¢=PG, L¢=L, N¢=N, ACL¢=ACL/{acl¢}.
● Создать субъект s¢, принадлежащий множеству групп g¢. Условие выполнения: g¢ÎG, s¢ÏS. Новое состояние системы: S¢=SÈ{s¢}, O¢=O, G¢=G/{g¢}È{g¢Ès¢}, PG¢=PG, L¢=L, N¢=N, ACL¢=ACL.
● Включить субъект s¢ в множество групп g¢. Условие выполнения: g¢ÎG, s¢ÎS, gÏSAs¢. Новое состояние системы: S¢=S, O¢=O, G¢=G/{g¢}È{g¢Ès¢}, PG¢=PG, L¢=L, N¢=N, ACL¢=ACL, SA¢s¢ = SAs’È/{g¢}.
● Исключить субъект s из множества групп g¢. Условие выполнения: g¢ÎSA, s¢ÎS. Новое состояние системы: S¢=S, O¢=O, G¢=G/{g¢}È{g¢/s¢}, PG¢=PG, L¢=L, ACL¢=ACL, SA¢s¢= SAs¢\{g¢}.
● Включить группу g¢ в множество привилегированных. Условие выполнения: g¢ÎG, g¢ÏPG. Новое состояние системы: S¢=S, O¢=O, G¢=G, PG¢=PGÈ{g¢}, L¢=L, N¢=N, ACL¢=ACL.
● Исключить группу g¢ из множества привилегированных. Условие выполнения: g¢ÎG, g¢ÎPG. Новое состояние системы: S¢=S, O¢=O, G¢=G, PG¢=PG\{g¢}, L¢=L, N¢=N, ACL¢=ACL.
● Уничтожить объект o¢. Условие выполнения: o¢ÎO. Новое состояние системы: S¢=S, O¢=O\{o¢}, G¢=G, PG¢=PG, L¢=L, N¢=N\({noc}È È{nol}), ACL¢=ACL.
● Уничтожить группу g¢. Условие выполнения: g¢ÎG. Новое состояние системы: S¢=S, O¢=O, G¢=G\{g¢}, PG¢=PG, T¢=T, L¢=L, N¢=N, C¢=C, PA¢=PA, SA¢=SA.
● Уничтожить субъект s¢. Условие выполнения: s¢ÎS. Новое состояние системы: S¢=S\{s¢}, O¢=O, G¢=G, PG¢=PG, L¢=L, N¢=N, ACL¢=ACL.
● Определить доступность права r¢ субъекта s¢ с уровнем доступа ls на объект o¢ с уровнем конфиденциальности lo¢.
Если (SAs’ÇPG)¹Æ, то Avail=1;
Иначе Avail=(tтекущее
При использовании данной модели процедура определения доступности объекта выглядит следующим образом.
Каждый субъект (пользователь МИС) входит в определенные группы. Группы могут быть привилегированными и непривилегированными. Каждая группа обладает определенным уровнем конфиденциальности. Права доступа субъектов определяются как совокупность прав, явно указанных ему, и прав, указанных для групп.
При попытке субъекта совершить определенную операцию над объектом происходит проверка доступности данной операции.
Если пользователь входит в одну из привилегированных групп, он имеет полный доступ к любому объекту.
Иначе происходит проверка меток времени. Если текущее время превышает предельное время доступа к объекту, субъект не имеет права изменять объект.
Следующим шагом является проверка явно указанных прав и меток конфиденциальности. Если одна из групп, в которые входит пользователь, обладает правами на данную операцию и уровень доступа субъекта больше либо равен уровню конфиденциальности объекта, доступ гарантируется. Вторым условием гарантии доступа является нали- чие возможности осуществления данной операции исходя из взаимоотношений между объектом и субъектом непосредственно (при этом не учитываются уровни конфиденциальности).
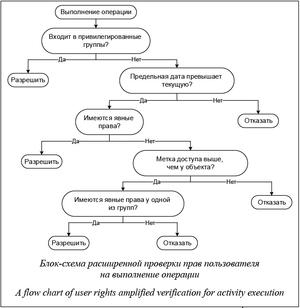 Таким образом, в системе заведомо заводятся необходимые группы со всеми атрибутами и списком прав доступа. Наличие меток конфиденциальности обусловливается обширным списком условий, по которым доступ должен или не должен предоставляться, а также большим количеством объектов. Разделение пользователей на группы необходимо для того, чтобы разграничивать права в зависимости от должности пользователя и места пребывания пациента.
Таким образом, в системе заведомо заводятся необходимые группы со всеми атрибутами и списком прав доступа. Наличие меток конфиденциальности обусловливается обширным списком условий, по которым доступ должен или не должен предоставляться, а также большим количеством объектов. Разделение пользователей на группы необходимо для того, чтобы разграничивать права в зависимости от должности пользователя и места пребывания пациента.
Для реализации представленной модели авторы предлагают использовать механизм триггеров, в которых должна быть реализована логика расширенной проверки прав пользователя на выполнение операции в соответствии с разработанной моделью.
Если пользователь имеет право выполнить инициированную им операцию, которая вызвала срабатывание триггера, операция беспрепятственно завершается, в противном случае операция отменяется (см. рисунок).
Для автоматизации процедуры создания и редактирования триггеров авторы разработали программу «Консоль администратора безопасности». Для удобства администрирования данная программа позволяет выполнять стандартные операции по управлению пользователями БД, а также дает возможность определять дополнительные параметры безопасности, предусмотренные предлагаемой моделью. При разработке программы использовались язык C# и технология .Net.
На взгляд авторов, применение предложенной модели позволит существенно сократить объем работы администратора безопасности и, как следствие, снизить вероятность возникновения ошибок настройки прав доступа.
Литература
1. Каталог медицинских информационных систем // Ассоциация развития медицинских информационных технологий. URL: http://www.armit.ru/catalog/ (дата обращения: 01.04.2015).
2. Гусев А., Романов Ф., Дуданов И. Медицинские информационные системы: анализ рынка // PCWeek/RussianEdition. 2005. № 47. С. 18–32.
3. Назаренко Г.И., Гулиев Я.И. Информационные системы в управлении лечебно-профилактическим учреждением // Врач и информационные технологии. 2006. № 4. С. 64–67.
4. Смольянинов В.Ю. Анализ условий предоставления и получения прав доступа в модели управления доступом MS SQL Server // Прикладная дискретная математика. 2014. № 2. С. 48–78.
5. Медведев Н.В., Гришин Г.А. Модели управления доступом в распределенных информационных системах // Наука и образование. 2011. № 01. С. 1–19; URL: http://technomag.bmstu. ru/doc/164245.html (дата обращения: 01.04.2015).
6. Гулиев Я.И., Фохт И.А., Фохт О.Я. [и др.]. Медицинские информационные системы и информационная безопасность. Проблемы и решения // Программные системы: Теория и приложения: тр. Междунар. конф. Переславль-Залесский. 2009. С. 175–206.
7. Гусев А.В. Медицинские информационные системы в России: текущее состояние, актуальные проблемы и тенденции развития // М.: Радиотехника. 2012. С. 157–170.
8. Назаренко Г.И., Михеев А.Е., Горбунов П.А., Гули- ев Я.И., Фохт И.А., Фохт О.А. Особенности решения проблем информационной безопасности в медицинских информационных системах // Врач и информационные технологии. 2007. № 4. С. 39–43.
9. Дабагов А.Р. Информатизация здравоохранения и некоторые проблемы построения интегрированных медицинских информационных систем // Журн. радиоэлектроники. 2011. № 9. С. 1–67.
10. Симаков О.В., Лебедев Г.С. Основные задачи информационно-телекоммуникационных технологий в здравоохранении Российской Федерации // Информационные технологии в медицине: тр. XI спец. конф.-выставки. М.: Радиотехника, 2010. С. 7–19.

