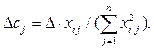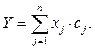Создание и внедрение систем поддержки принятия решений является критической технологией, развитие которой напрямую влияет на социальное благополучие населения. В связи с общей информатизацией лечебных учреждений применение информационных систем для решения задач медицины является приоритетным направлением, так как возрастающие объемы информации, совершенствование методик диагностики и внедрение новых методик лечения расширяют задачи по обработке и интерпретации данных. Огромное значение приобретают системы, способные моделировать опыт квалифицированных специалистов, так как применение таких систем позволяет повысить качество диагностики и проследить эффективность предложенного лечения.
Одной из острых проблем является лечение вирусных гепатитов. По данным ВОЗ, более 200 миллионов человек больны хронической формой гепатита. В Российской Федерации ситуация с гепатитом наиболее сложная. В отдельных районах вирус приобретает эпидемический характер. Заболевание наносит огромный урон экономике страны, поскольку лечение хронических форм зачастую не приносит ожидаемого результата и заключается в поддержании здоровья на достаточном уровне.
Сложность в диагностике гепатита обусловлена наличием большого количества нозологических форм, которые характеризуются различными механизмами заражения, клиническими проявлениями, патогенезом, иммуногенезом, тяжестью течения и применяемыми методами диагностики. Даже при своевременной и правильной диагностике существуют огромные сложности с подбором лечения и контролем его эффективности.
Первоначальным методом диагностики болезни является тщательный сбор анамнеза [1], в котором особое внимание стоит обратить на факторы риска: употребление пациентом алкоголя и наркотиков, наличие беспорядочных половых контактов и парентеральных вмешательств, а также выявление в истории семьи случаев инфицирования вирусом гепатита и возникновения рака печени. Полученная информация может использоваться эпидемиологами для проведения необходимых мероприятий: выявление источника инфекции, работа с контактными лицами и т.д. [2].
 В качестве входных используются значения 65 факторов, заключающих в себе данные анамнеза, УЗИ, серологических маркеров и биохимии крови. Основной задачей в определении нозологической формы по входным данным является их правильная интерпретация, поскольку для неподготовленного человека она может представлять значительную сложность. Рабочее окно системы показано на рисунке 1.
В качестве входных используются значения 65 факторов, заключающих в себе данные анамнеза, УЗИ, серологических маркеров и биохимии крови. Основной задачей в определении нозологической формы по входным данным является их правильная интерпретация, поскольку для неподготовленного человека она может представлять значительную сложность. Рабочее окно системы показано на рисунке 1.
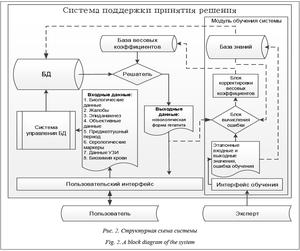
Система реализована в среде разработки Embarcadero Delphi, в качестве сервера БД использован FirebirdSQL. Структурная схема системы поддержки принятия решения приведена на ри- сунке 2, в схеме присутствуют основной модуль – решатель и модуль обучения, который задействуется только при формировании весовых коэффици- ентов.
Для вирусов гепатита характерна огромная нозологическая вариабельность. Рассматривая только вирусный гепатит С, можно выделить 6 основных генотипов и более 90 субтипов, для каждого из них характерен определенный ареал обитания [3].
Для диагностики наиболее правильным с точки зрения медицины является использование классификации гепатита по международной системе классификации МКБ-10 [4], однако данная классификация вносит определенную сложность при создании системы диагностики, так как требует огромной обучающей выборки. Наиболее верным решением является выделение самых распространенных форм: острый гепатит А, хронический гепатит В (интеграция), хронический гепатит С (латентная фаза) и хронический гепатит С (реактивация).
 Топология системы представляет собой вариацию рекуррентной нейронной сети (рис. 3), обучение которой заключается в расчете весовых коэффициентов. Алгоритм обучения представляет собой модификацию алгоритма Качмажа для решения систем линейных уравнений [5, 6]. На начальном этапе предъявляется образ в виде линейной матрицы значений, которая при большом числе образов становится прямоугольной:
Топология системы представляет собой вариацию рекуррентной нейронной сети (рис. 3), обучение которой заключается в расчете весовых коэффициентов. Алгоритм обучения представляет собой модификацию алгоритма Качмажа для решения систем линейных уравнений [5, 6]. На начальном этапе предъявляется образ в виде линейной матрицы значений, которая при большом числе образов становится прямоугольной:
X = (x1, …, xn). (1)
Выходные значения, характеризующие нозологическую форму, рассчитываются при помощи алгебраического суммирования произведений входного образа на весовые коэффициенты:
Y =  где cj – весовой коэффициент уравнения.
где cj – весовой коэффициент уравнения.
Полученное выходное значение Ypi сравнивается с заданным Yзi, разница составляет ошибку:
D = Yзi – Ypi.. (2)
При значениях ошибки (2), меньших допустимой, система считается обученной, в альтернативном случае происходит пересчет весовых коэффициентов. Поправка к весовому коэффициенту рассчитывается при предъявлении входного образа и ошибки обучения: 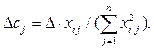
Расчет весовых коэффициентов прекращается при достижении ошибкой (2) удовлетворяющих значений, заданных до обучения. График обучения рассматриваемой системы показан на рисунке 4. Выходное значение системы, характеризующее нозологическую форму гепатита, после обучения рассчитывается по уравнению 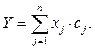
 Данный алгоритм уже хорошо зарекомендовал себя при решении задачи реконструкции компьютерной томографии [7]. Его существенным ограничением является невозможность решения задачи при неполных данных, вследствие чего матрица становится нелинейной или в нее вносятся искажения. Однако путем модификации алгоритма данная проблема разрешима [8].
Данный алгоритм уже хорошо зарекомендовал себя при решении задачи реконструкции компьютерной томографии [7]. Его существенным ограничением является невозможность решения задачи при неполных данных, вследствие чего матрица становится нелинейной или в нее вносятся искажения. Однако путем модификации алгоритма данная проблема разрешима [8].
Формирование весовых коэффициентов в системе происходило путем представления значений 280 образов, содержащих данные пациентов, больных различными формами гепатита.
Проведенные исследования системы позволяют выявить, что при предъявлении образов с наибольшей ошибкой обучающая выборка системы для каждой нозологической формы может составлять 25–30 примеров.
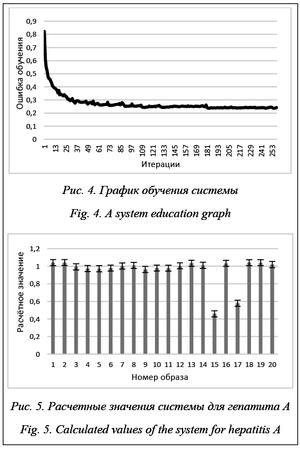
Апробация системы происходила на выборке из 100 образов, коэффициент корреляции оценок системы с оценками врача для полных образов составил 0,7. На рисунке 5 представлены расчетные значения для 20 образов, характеризующих пациентов, больных гепатитом А, не участвующих в обучении си- стемы. Эталонное значение равно 1. Из гистограммы можно заметить, что в рассматриваемом случае коэффициент корреляции составляет 0,9.
Применение описанного подхода позволит повысить качество диагностики гепатитов в лечебно-профилактических учреждениях и, соответственно, эффективность лечения. Рассмотренный алгоритм также может применяться в медицине для определения эффективности лечения [9], распознавания данных сцинтиграфических изображений [10] и для других целей.
Литература
1. Di Bisceglie A.M., Order S.E., Klein J.L. The role of chronic viral hepatitis in hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States. Am. J. Gastroenterol, 1991, vol. 86, pp. 335–338.
2. Пименов Н.Н., Чуланов В.П., Комарова С.В., Карандашова И.В., Неверов А.Д., Михайловская Г.В., Долгин В.А., Лебедева Е.Б., Пашкина К.В., Коршунова Г.С. Гепатит С в России: эпидемиологическая характеристика и пути совершенствования диагностики и надзора // Эпидемиология и инфекционные болезни. 2012. № 3. С. 4–10.
3. Simmonds P., Bukh J., Combet C. et al. Consensus proposals for a unified system of nomenclature of hepatitis C virus genotypes. Hepatology, 2005, vol. 42, no. 4, pp. 962–973.
4. Асадов Д.А. Клиническое руководство по диагностике, лечению и профилактике хронических гепатитов у взрослых в первичном звене здравоохранения. Ташкент, 2013. 47 с.
5. Kaczmarz S. Approximate solution of systems of linear equations. Internat. J. Control, 1993, vol. 57, no. 6, pp. 1269–1271.
6. Ильин В.П. Об итерационном методе Качмажа и его обобщениях // Сибирский журнал индустриальной математики. 2006. Т. 9. № 3. С. 39–49.
7. Gordon R., Herman G. Reconstruction of pictures from their projections. Communications of the ACM. 1971, vol. 14, no. 12, pp. 759–768.
8. Иванов А.А. Решение задачи полиномиальной аппроксимации с использованием итерационного метода Качмажа // Вестн. СГАУ. 2008. № 2. С. 179–182.
9. Астафьев А.Н., Кавыгин В.В. Нейронная сеть для оценки эффективности лечения гепатита // Медико-экологические информационные технологии-2016: сб. тр. XIX Междунар. науч.-технич. конф. Курск: Изд-во ЮЗТУ, 2016. С. 68–74.
10. Астафьев А.Н., Кавыгин В.В. Нейронная сеть с направленной активацией нейронных элементов // Актуальные вопросы науки: матер. XХV Междунар. науч.-практич. конф. М.: Спутник +, 2016. С. 155–158.
References
- Di Bisceglie A.M., Order S.E., Klein J.L. The role of chronic viral hepatitis in hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States. Am. Jour. Gastroenterol. 1991, vol. 86, pp. 335–338.
- Pimenov N.N., Chulanov V.P., Komarova S.V., Karandashova I.V., Neverov A.D., Mikhaylovskaya G.V., Dolgin V.A., Lebede-
va E.B., Pashkina K.V., Korshunova G.S. Hepatitis C in Russia: epidemiological characteristics and ways to improve diagnosis and monitoring. Epidemiologiya i infektsionnye bolezni [Epidemiology and Infectious Diseases]. 2012, no. 3, pp. 4–10 (in Russ.).
- Simmonds P., Bukh J., Combet C. Consensus proposals for a unified system of nomenclature of hepatitis C virus genotypes. Hepatology. 2005, vol. 42, no. 4, pp. 962–973.
- Asadov D.A. Klinicheskoe rukovodstvo po diagnostike, lecheniyu i profilaktike khronicheskikh gepatitov u vzroslykh v pervichnom zvene zdravookhraneniya [Clinical Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Chronic Hepatitis B in Adults in Primary Care]. Tashkent, 2013, 47 p.
- Kaczmarz S. Approximate solution of systems of linear equations. Int. Jour. Control. 1993, vol. 57, no. 6, pp. 1269–1271.
- Ilin V.P. On the iterative Kaczmarz method and its generalizations. Sibirsky zhurnal industrialnoy matematiki [Jour. of Applied and Industrial Mathematics]. 2006, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 39–49 (in Russ.).
- Gordon R., Herman G. Reconstruction of pictures from their projections. Communications of the ACM. 1971, vol. 14, no. 12, pp. 759–768.
- Ivanov A.A. Solving the polynomial approximation problem with use of the iterative kachmazh method. Vestnik SGAU [Vestnik of Samara Univ. Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering]. 2008, no. 2, pp. 179–182 (in Russ.).
- Astafyev A.N., Kavygin V.V. A neural network for assessing the efficacy of hepatitis treatment. Mediko-ekologicheskie informatsionnye tekhnologii-2016: sb. tr. XIX Mezhdunar. nauch.-tekhnich. konf. [Medical-Ecological Information Technologies-2016: 19th Int. Scientific and Tech. Conf.]. Kursk, 2016, pp. 68–74 (in Russ.).
- Astafyev A.N., Kavygin V.V. Neural network with targeted activation of neural cells. Aktualnye voprosy nauki: mater. XXV Mezhdunar. nauch.-praktich. konf. [Topical Issues of Science: Proc. 15th Int. Scientific and Practical Conf.]. Moscow, Sputinik+ Publ., 2016, pp. 155–158 (in Russ.).



 где cj – весовой коэффициент уравнения.
где cj – весовой коэффициент уравнения.