Во многих отраслях промышленности и техники широко применяется водород. Это самый подвижный из всех газов, поэтому в большинстве технологических операций неизбежны процессы сорбции водорода металлом, которые могут протекать при любых температурных режимах. Проникновение водорода в металлы влияет на прочностные свойства конструкций. Замечено, что элементы конструкций с дефектами, порами и трещинами, попадая в среду с водородом, на- чинают быстро разрушаться. Согласно [1], это объясняется тем, что атомарный водород, диффундируя в металле и проникая в дефекты, ас- социируется в менее активный молекулярный водород, теряет способность к диффузии, накапливается в дефекте и создает избыточное давление. Таким образом, рассматривая взаимодействие атомов водорода и дефектов, при построении модели имеет смысл учитывать влияние на процесс диффузии как внешнего напряжения, так и внутреннего, вызванного скоплением молекулярного водорода в дефектах.
Математическая модель деформирования в водородосодержащей среде
Рассмотрим конечную двухмерную область W, содержащую дефекты (поры и трещины), расположенные случайным образом. Область граничит с водородосодержащей средой и подвержена внешнему механическому нагружению. Поставим задачу оценки влияния внешнего напряжения на давление, создаваемое водородом в дефектах.
В качестве модели происходящих процессов примем связную диффузионно-деформационную задачу, описываемую уравнениями
 , xÎW; (1)
, xÎW; (1)
 , xÎW, (2)
, xÎW, (2)
а также начальными и граничными условиями
 , xÎW;
, xÎW;
c(x, t)=c*(x, t), xÎГ; (3)
f(x, t, c)=f*(x, t, c), xÎГf;
u(x, t)=u*(x, t), xÎГu. (4)
Здесь с(x, t) – концентрация водорода в точке x(x1, x2) в момент времени t³t0; t0 – начальный момент времени; D – коэффициент диффузии;  – оператор Лапласа; VH – парциальный молярный объем водорода в металле; R – газовая постоянная; T – абсолютная температура; s – среднее нормальное напряжение; Ñ=(¶/¶x1, ¶/¶x2) – градиент функции; Ñs×Ñc – скалярное произведение векторов; r – массовая плотность материала; u(u1, u2) – вектор перемещений; l и m – коэффициенты Ламе; f(x, t, c) – вектор поверхностных напряжений; Г=Гf ÈГu – граница области W. Звездочкой отмечены заданные начальные и граничные значения.
– оператор Лапласа; VH – парциальный молярный объем водорода в металле; R – газовая постоянная; T – абсолютная температура; s – среднее нормальное напряжение; Ñ=(¶/¶x1, ¶/¶x2) – градиент функции; Ñs×Ñc – скалярное произведение векторов; r – массовая плотность материала; u(u1, u2) – вектор перемещений; l и m – коэффициенты Ламе; f(x, t, c) – вектор поверхностных напряжений; Г=Гf ÈГu – граница области W. Звездочкой отмечены заданные начальные и граничные значения.
Характерное время протекания диффузионного и деформационного процессов существенно различается, поэтому на некотором временном шаге при диффузии механическое движение можно считать установившимся. В связи с этим решение связной задачи осуществлялось по шагам по времени в соответствии со следующим алгоритмом. Интервал времени [t0, tK], где tK – конечный момент времени, разбит на K шагов [tk-1, tk] (k=1, …, K). Каждый шаг по времени включает в себя четыре этапа решения.
Этап 1. Решается деформационная задача в рамках линейной теории упругости, описываемая уравнением
(l+m)Ñ(divu)+mDu=0, xÎW (5)
со сложившимися к текущему шагу статическими граничными условиями, заданными в напряжениях
f(x, c)=P1*(x, c), xÎГ1;
f(x)=P2*(x), xÎГ2, (6)
где Г1 – внутренняя граница области, разделяющая сплошной материал и дефекты; Г2 – внешняя граница области; Г=Г1ÈГ2; P1* – внутреннее давление в дефектах; P2* – внешнее механическое напряжение, действующее на внешней границе области. На первом шаге по времени P1*=0, на каждом последующем временном шаге P1* определяется из решения диффузионной задачи на предыдущем шаге. В результате решения задачи (5), (6) внутри области W определяются значения перемещений, напряжений и пространственных производных от напряжений, необходимые для вычисления градиента Ñσ.
Решение статической задачи теории упругости осуществлялось с помощью модифицированного метода граничных элементов (МГЭ) [2]. Используемые при реализации МГЭ криволинейные интегралы вычислялись по аналитическим формулам из [2]. Получение таких формул позволяет включить их в алгоритм, повысив его универсальность. Кроме того, аналитическое интегрирование по сравнению с численным имеет очевидные преимущества по точности и скорости вычислений. Его применение дает ускорение счета в 5–10 раз, а выигрыш в точности соответствует погрешности интерполяции, применяемой при численном интегрировании. Применение предложенной методики позволяет во многом избежать традиционных вычислительных трудностей, возникающих при численной реализации операций интегрирования и дифференцирования, необходимых, в частности, в рассматриваемой задаче для вычисления производных компонент тензора напряжений. Еще одним преимуществом МГЭ является возможность распараллеливания вычислений на всех этапах решения [2].
Этап 2. Рассматривается двухмерная диффузионная задача с учетом влияния напряженного состояния, описываемая уравнением (1) при ус- ловиях (3). Решение данной задачи в работе осуществлялось модифицированным МГЭ применительно к задачам параболического типа [3]. Соответствующее задаче (1), (3) граничное интегральное уравнение имеет вид [4]


 . (7)
. (7)
Здесь x0(x01, x02) – произвольная граничная точка области W; q(x, t)=–¶c(x, t)/¶n(x) – диффузионный поток через границу, заданную положением внешней нормали n(x); величина 
 принимается в качестве неоднородности; функции влияния G*(x0, x, tK, t) и F*(x0, x, tK, t) для двухмерной задачи диффузии определяются в виде
принимается в качестве неоднородности; функции влияния G*(x0, x, tK, t) и F*(x0, x, tK, t) для двухмерной задачи диффузии определяются в виде
 ,
,
r2=zizi, zi=xi–x0i, i=1, 2;
 .
.
 Поскольку при удалении от дефекта градиент напряжения быстро убывает, функцию y(x, t) можно учитывать только в зонах влияния – окрестностях дефектов, за границами которых градиент напряжений пренебрежимо мал. Для вычисления в произвольный момент времени интегралов по граничным элементам, необходимых для решения граничного интегрального уравнения и для вычисления концентрации и ее пространственных производных внутри области, были получены аналитические формулы. При этом рассматривались различные виды аппроксимации на прямолинейном граничном элементе, в том числе аппроксимация, основанная на граничноэлементном решении одномерной задачи диффузии для элемен- та [3].
Поскольку при удалении от дефекта градиент напряжения быстро убывает, функцию y(x, t) можно учитывать только в зонах влияния – окрестностях дефектов, за границами которых градиент напряжений пренебрежимо мал. Для вычисления в произвольный момент времени интегралов по граничным элементам, необходимых для решения граничного интегрального уравнения и для вычисления концентрации и ее пространственных производных внутри области, были получены аналитические формулы. При этом рассматривались различные виды аппроксимации на прямолинейном граничном элементе, в том числе аппроксимация, основанная на граничноэлементном решении одномерной задачи диффузии для элемен- та [3].
Использование аналитических формул интегрирования дает те же преимущества, что и для задач теории упругости. Интеграл по области W находится численно на основе разбиения области на конечные элементы.
Этап 3. Вычисляется давление молекулярного водорода в каждом из дефектов в предположении, что молекулярный водород удовлетворяет уравнению состояния идеального газа:
 , (8)
, (8)
где m – масса водорода в дефекте; M, VM – молярная масса и молярный объем газа. Масса водорода в дефекте равна количеству водорода, поступающего в дефект за время шага Dt=tk–tk-1, и полному потоку водорода через границу дефекта
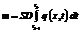 , (9)
, (9)
где S – площадь поверхности дефекта.
 Этап 4. Проверяется условие разрушения границы каждого дефекта. Для этого внутреннее давление водорода в дефекте сравнивается с критическим давлением [1] на предмет выполнения неравенства
Этап 4. Проверяется условие разрушения границы каждого дефекта. Для этого внутреннее давление водорода в дефекте сравнивается с критическим давлением [1] на предмет выполнения неравенства
 . (10)
. (10)
Здесь Pкp – критическое давление, при котором наступает разрушение материала; sT – предел текучести материала; eкр – критическая деформация; sкр – величина критического напряжения, при котором начинает развиваться дефект. Для реальных сталей принимается, что Pкp>3sT. Если критическое давление не достигнуто, расчеты продолжаются на следующем временном шаге с учетом перерасчета граничных условий деформационной задачи.
Описание программы
На базе разработанного алгоритма создана компьютерная программа для моделирования влияния водорода на прочностные свойства плоских деталей металлических конструкций. Блок-схема программы представлена на рисунке 1.
 Программа состоит из графического редактора и расчетного модуля. Графический редактор ввода данных написан на языке программирования Java и работает под операционными системами Windows и Linux. Инструментальные средства редактора позволяют строить геометрическую модель плоской области с внутренними дефектами (порами и трещинами), задавать краевые условия, физические параметры процесса, а также внутреннюю область для расчета. Внешняя граница и внутренняя область моделируются замкнутыми ломаными линиями, отдельные звенья которых могут быть дугами окружностей. Расположение дефектов может и задаваться пользователем, и определяться случайным вероятностным распределением. Для редактирования построенной области используются операции перемещения всей области, добавления, удаления или перемещения отдельных вершин, имеется также и возможность изменения масштаба координатной сетки. Для большей наглядности все геометрические и физические параметры процесса, краевые условия задачи заносятся в таблицы и легко редактируются. После ввода входные данные преобразуются в специальный формат для их дальнейшей обработки.
Программа состоит из графического редактора и расчетного модуля. Графический редактор ввода данных написан на языке программирования Java и работает под операционными системами Windows и Linux. Инструментальные средства редактора позволяют строить геометрическую модель плоской области с внутренними дефектами (порами и трещинами), задавать краевые условия, физические параметры процесса, а также внутреннюю область для расчета. Внешняя граница и внутренняя область моделируются замкнутыми ломаными линиями, отдельные звенья которых могут быть дугами окружностей. Расположение дефектов может и задаваться пользователем, и определяться случайным вероятностным распределением. Для редактирования построенной области используются операции перемещения всей области, добавления, удаления или перемещения отдельных вершин, имеется также и возможность изменения масштаба координатной сетки. Для большей наглядности все геометрические и физические параметры процесса, краевые условия задачи заносятся в таблицы и легко редактируются. После ввода входные данные преобразуются в специальный формат для их дальнейшей обработки.
Расчетный модуль программы написан на языке программирования C с использованием библиотеки параллельных вычислений MPI и включает в себя непосредственно алгоритм расчета. При запуске модуля задается число вычислительных ядер на кластере, кратное числу точек разбиения границы области. Выходные данные формируются в виде таблицы Excel.
 В качестве иллюстрации применения программы была рассмотрена двухмерная задача растяжения в водородосодержащей среде прямоугольной области l´d с внутренним дефектом – порой радиуса a, расположенной в центре детали (рис. 2). Выбор в качестве механического воздействия продольного растяжения обусловлен тем, что при растяжении происходит быстрое разрушение материала области и интересующие характеристики водородного охрупчивания проявляются в полной мере. На внешней границе приложено постоянное во времени растягивающее напряжение P2*. Задача решена в нескольких вариантах при следующих значениях параметров: l=20 м; d=10 м; a=0,5 м; E=2×1011 H/м2; v=0,28; P2*=106 H/м2; c0*=0; c*=20 моль/л; D=4,3×10-9 м2/с; R=8,3 Дж/(моль×К); VH=2×10-6 м3/моль; VМ=22,4×10-3 м3/моль; М=2,016 г/моль; T=295 K; sT=250×106 H/м2.
В качестве иллюстрации применения программы была рассмотрена двухмерная задача растяжения в водородосодержащей среде прямоугольной области l´d с внутренним дефектом – порой радиуса a, расположенной в центре детали (рис. 2). Выбор в качестве механического воздействия продольного растяжения обусловлен тем, что при растяжении происходит быстрое разрушение материала области и интересующие характеристики водородного охрупчивания проявляются в полной мере. На внешней границе приложено постоянное во времени растягивающее напряжение P2*. Задача решена в нескольких вариантах при следующих значениях параметров: l=20 м; d=10 м; a=0,5 м; E=2×1011 H/м2; v=0,28; P2*=106 H/м2; c0*=0; c*=20 моль/л; D=4,3×10-9 м2/с; R=8,3 Дж/(моль×К); VH=2×10-6 м3/моль; VМ=22,4×10-3 м3/моль; М=2,016 г/моль; T=295 K; sT=250×106 H/м2.
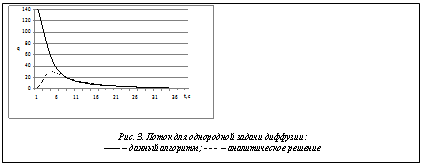
На рисунках 3−6 отражены результаты решения задачи. На рисунке 3 сравнивается диффузионный поток на границе области, подсчитанный для однородного уравнения диффузии по предложенному алгоритму и с помощью аналитического решения [5]. Рисунок 4 иллюстрирует изменение диффузионного потока на поверхности поры во времени с учетом и без учета внешних растягивающих напряжений. Рисунок 5 демонстрирует изменение давления молекулярного водорода в поре без учета внутреннего напряженного состояния материала, а рисунок 6 – изменение внутреннего давления в поре под действием внешних растягивающих напряжений для двух случаев: когда механическая задача решается без учета давления молекулярного водорода в поре и с учетом давления.
 На основании изложенного можно сделать следующие выводы. Близость графиков на рисунке 3 показывает хорошую согласованность результатов расчетов с аналитическим решением. Отклонение результатов расчетов от аналитического решения вблизи начального момента времени обусловлено тем, что принятый в качестве аналитического решения ряд дает на этом интервале плохое приближение [5]. Как видно из графиков на рисунках 4 и 5, учет напряженного состояния для двухмерной задачи диффузии необходим, причем под действием внешнего растягивающего напряжения диффузионный процесс существенно ускоряется. График на рисунке 6 характеризует влияние диффузионного процесса на механическую задачу в околопоровой зоне. Из рисунков видно, что характер роста давления в поре для решения однородной задачи диффузии и для решения связной диффузионно-деформационной задачи различен. Таким образом, для анализа прочности плоских деталей металлических конструкций с дефектами необходимо учитывать как внутреннее напряжение в дефектах вследствие процесса диффузии, так и внешнее механическое напряжение вследствие процесса деформации. Представленный в работе алгоритм и программа учитывают оба этих фактора.
На основании изложенного можно сделать следующие выводы. Близость графиков на рисунке 3 показывает хорошую согласованность результатов расчетов с аналитическим решением. Отклонение результатов расчетов от аналитического решения вблизи начального момента времени обусловлено тем, что принятый в качестве аналитического решения ряд дает на этом интервале плохое приближение [5]. Как видно из графиков на рисунках 4 и 5, учет напряженного состояния для двухмерной задачи диффузии необходим, причем под действием внешнего растягивающего напряжения диффузионный процесс существенно ускоряется. График на рисунке 6 характеризует влияние диффузионного процесса на механическую задачу в околопоровой зоне. Из рисунков видно, что характер роста давления в поре для решения однородной задачи диффузии и для решения связной диффузионно-деформационной задачи различен. Таким образом, для анализа прочности плоских деталей металлических конструкций с дефектами необходимо учитывать как внутреннее напряжение в дефектах вследствие процесса диффузии, так и внешнее механическое напряжение вследствие процесса деформации. Представленный в работе алгоритм и программа учитывают оба этих фактора.
Литература
1. Андрейкив А.Е., Панасюк В.В., Поляков Л.И., Харин В.С. Механика водородного охрупчивания металлов и расчет элементов конструкций на прочность. Львов: препр. № 133. Физ.-мех. ин-т им. Г.В. Карпенко. 1987. 50 с.
2. Федотов В.П., Спевак Л.Ф. Модифицированный метод граничных элементов в задачах механики, теплопроводности и диффузии. Екатеринбург: УрО РАН, 2009. 164 с.
3. Нефедова О.А., Федотов В.П. Применение модифицированного метода граничных элементов для решения задач теплопроводности / Актуальные проблемы современной науки: тр. 5-го Междунар. форума молод. ученых. Самара: СамГТУ, 2010. С. 143–147.
4. Бреббия К., Теллес Ж., Вроубел Л. Метод граничных элементов. М.: Мир, 1987. 526 с.
5. Лыков А.В. Теория теплопроводности. М.: Высш. шк. 1967. 600 с.
 , xÎW; (1)
, xÎW; (1) , xÎW, (2)
, xÎW, (2) , xÎW;
, xÎW; – оператор Лапласа; VH – парциальный молярный объем водорода в металле; R – газовая постоянная; T – абсолютная температура; s – среднее нормальное напряжение; Ñ=(¶/¶x1, ¶/¶x2) – градиент функции; Ñs×Ñc – скалярное произведение векторов; r – массовая плотность материала; u(u1, u2) – вектор перемещений; l и m – коэффициенты Ламе; f(x, t, c) – вектор поверхностных напряжений; Г=Гf ÈГu – граница области W. Звездочкой отмечены заданные начальные и граничные значения.
– оператор Лапласа; VH – парциальный молярный объем водорода в металле; R – газовая постоянная; T – абсолютная температура; s – среднее нормальное напряжение; Ñ=(¶/¶x1, ¶/¶x2) – градиент функции; Ñs×Ñc – скалярное произведение векторов; r – массовая плотность материала; u(u1, u2) – вектор перемещений; l и m – коэффициенты Ламе; f(x, t, c) – вектор поверхностных напряжений; Г=Гf ÈГu – граница области W. Звездочкой отмечены заданные начальные и граничные значения.

 . (7)
. (7)
 принимается в качестве неоднородности; функции влияния G*(x0, x, tK, t) и F*(x0, x, tK, t) для двухмерной задачи диффузии определяются в виде
принимается в качестве неоднородности; функции влияния G*(x0, x, tK, t) и F*(x0, x, tK, t) для двухмерной задачи диффузии определяются в виде ,
, .
.  Поскольку при удалении от дефекта градиент напряжения быстро убывает, функцию y(x, t) можно учитывать только в зонах влияния – окрестностях дефектов, за границами которых градиент напряжений пренебрежимо мал. Для вычисления в произвольный момент времени интегралов по граничным элементам, необходимых для решения граничного интегрального уравнения и для вычисления концентрации и ее пространственных производных внутри области, были получены аналитические формулы. При этом рассматривались различные виды аппроксимации на прямолинейном граничном элементе, в том числе аппроксимация, основанная на граничноэлементном решении одномерной задачи диффузии для элемен- та [3].
Поскольку при удалении от дефекта градиент напряжения быстро убывает, функцию y(x, t) можно учитывать только в зонах влияния – окрестностях дефектов, за границами которых градиент напряжений пренебрежимо мал. Для вычисления в произвольный момент времени интегралов по граничным элементам, необходимых для решения граничного интегрального уравнения и для вычисления концентрации и ее пространственных производных внутри области, были получены аналитические формулы. При этом рассматривались различные виды аппроксимации на прямолинейном граничном элементе, в том числе аппроксимация, основанная на граничноэлементном решении одномерной задачи диффузии для элемен- та [3]. , (8)
, (8)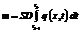 , (9)
, (9) Этап 4. Проверяется условие разрушения границы каждого дефекта. Для этого внутреннее давление водорода в дефекте сравнивается с критическим давлением [1] на предмет выполнения неравенства
Этап 4. Проверяется условие разрушения границы каждого дефекта. Для этого внутреннее давление водорода в дефекте сравнивается с критическим давлением [1] на предмет выполнения неравенства . (10)
. (10) Программа состоит из графического редактора и расчетного модуля. Графический редактор ввода данных написан на языке программирования Java и работает под операционными системами Windows и Linux. Инструментальные средства редактора позволяют строить геометрическую модель плоской области с внутренними дефектами (порами и трещинами), задавать краевые условия, физические параметры процесса, а также внутреннюю область для расчета. Внешняя граница и внутренняя область моделируются замкнутыми ломаными линиями, отдельные звенья которых могут быть дугами окружностей. Расположение дефектов может и задаваться пользователем, и определяться случайным вероятностным распределением. Для редактирования построенной области используются операции перемещения всей области, добавления, удаления или перемещения отдельных вершин, имеется также и возможность изменения масштаба координатной сетки. Для большей наглядности все геометрические и физические параметры процесса, краевые условия задачи заносятся в таблицы и легко редактируются. После ввода входные данные преобразуются в специальный формат для их дальнейшей обработки.
Программа состоит из графического редактора и расчетного модуля. Графический редактор ввода данных написан на языке программирования Java и работает под операционными системами Windows и Linux. Инструментальные средства редактора позволяют строить геометрическую модель плоской области с внутренними дефектами (порами и трещинами), задавать краевые условия, физические параметры процесса, а также внутреннюю область для расчета. Внешняя граница и внутренняя область моделируются замкнутыми ломаными линиями, отдельные звенья которых могут быть дугами окружностей. Расположение дефектов может и задаваться пользователем, и определяться случайным вероятностным распределением. Для редактирования построенной области используются операции перемещения всей области, добавления, удаления или перемещения отдельных вершин, имеется также и возможность изменения масштаба координатной сетки. Для большей наглядности все геометрические и физические параметры процесса, краевые условия задачи заносятся в таблицы и легко редактируются. После ввода входные данные преобразуются в специальный формат для их дальнейшей обработки. В качестве иллюстрации применения программы была рассмотрена двухмерная задача растяжения в водородосодержащей среде прямоугольной области l´d с внутренним дефектом – порой радиуса a, расположенной в центре детали (рис. 2). Выбор в качестве механического воздействия продольного растяжения обусловлен тем, что при растяжении происходит быстрое разрушение материала области и интересующие характеристики водородного охрупчивания проявляются в полной мере. На внешней границе приложено постоянное во времени растягивающее напряжение P2*. Задача решена в нескольких вариантах при следующих значениях параметров: l=20 м; d=10 м; a=0,5 м; E=2×1011 H/м2; v=0,28; P2*=106 H/м2; c0*=0; c*=20 моль/л; D=4,3×10-9 м2/с; R=8,3 Дж/(моль×К); VH=2×10-6 м3/моль; VМ=22,4×10-3 м3/моль; М=2,016 г/моль; T=295 K; sT=250×106 H/м2.
В качестве иллюстрации применения программы была рассмотрена двухмерная задача растяжения в водородосодержащей среде прямоугольной области l´d с внутренним дефектом – порой радиуса a, расположенной в центре детали (рис. 2). Выбор в качестве механического воздействия продольного растяжения обусловлен тем, что при растяжении происходит быстрое разрушение материала области и интересующие характеристики водородного охрупчивания проявляются в полной мере. На внешней границе приложено постоянное во времени растягивающее напряжение P2*. Задача решена в нескольких вариантах при следующих значениях параметров: l=20 м; d=10 м; a=0,5 м; E=2×1011 H/м2; v=0,28; P2*=106 H/м2; c0*=0; c*=20 моль/л; D=4,3×10-9 м2/с; R=8,3 Дж/(моль×К); VH=2×10-6 м3/моль; VМ=22,4×10-3 м3/моль; М=2,016 г/моль; T=295 K; sT=250×106 H/м2.
